Search Engine Optimization Overview
Search Engine Optimization, also known as SEO, is how a website can be improved or optimized so it ranks higher by search engines. By improving a site’s visibility in search engines and focusing on how the search engine algorithm measures a website, a site can have better results in the /Search Engine Results Page (SERP). The constant evolution of Google’s algorithm requires vigilant attention to changes in SEO strategies. In the past, cheating the system by using /black hat techniques has resulted in manual penalties and de-indexation. One must create content that is searchable, shareable, and linkable to avoid risk. It is vital to put a focus on creating websites and pages for users, not websites. Today’s search has more things in common with creating a good user experience than pandering to robots.
How Search Engines Work
Search engines use robots/spiders/crawlers to scan the internet, indexing the pages in a large database usually /relational or /Bigtable. These crawlers go from site to site following the links on each site, both internal and external. These sites are then sorted by their content, usability, and other factors.
Search Engine Algorithm
When a keyword is searched for on a search engine, an algorithm that takes /over 200 factors into consideration is used to query the database to find the best results. These algorithms are constantly being tested and improved so that the best results can appear in the search engine results page. In recent years, /Google has created updates to fight spam and serve the best webpages possible. Some things that these updates focus on are duplicate content, paid links, and using black hat techniques.
Major Google Algorithm Updates
There’s a handful of major Google algorithm updates responsible for dramatic sea changes in SEO. Here’s a brief overview of some of the most influential algorithms.
Mobile
As recently as 2016, studies showed more people were accessing the internet from mobile devices than traditional desktop computers. Google’s mobile-friendly update was designed to address this significant milestone—a mobile-based web required mobile-based search results to better serve Google users. Whereas having a mobile-friendly website used to be considered an advantage in SEO, it’s now universally regarded as essential.
Panda
The quality of a website’s content became a major focus with Google’s Panda update. Sites with shallow content or excessive amounts of duplicate content (scraped from other parts of the web, recycled throughout the site itself, etc.) saw rankings negatively impacted. Panda forced websites to prioritize content marketing if they wanted to rank competitively, dramatically improving the quality of individual results for Google searchers.
Penguin
Backlinks, or external links, have always played a critical role in SEO. But, Google’s Penguin update radically redefined their responsibilities. The update changed the game by determining the quality of links when ranking sites—not just the quantity of links. Websites could no longer manipulate search rankings by building tons of spammy, low-quality backlinks; sites with links from trustworthy, relevant sites improved.
Pigeon
Google’s local algorithm update helped provide more useful, relevant, and topical search results to users based on their search location. The update dramatically refined Google’s distance and location ranking parameters—it’s the reason we can search ‘pizza near me’ and get a list of results just down the road.
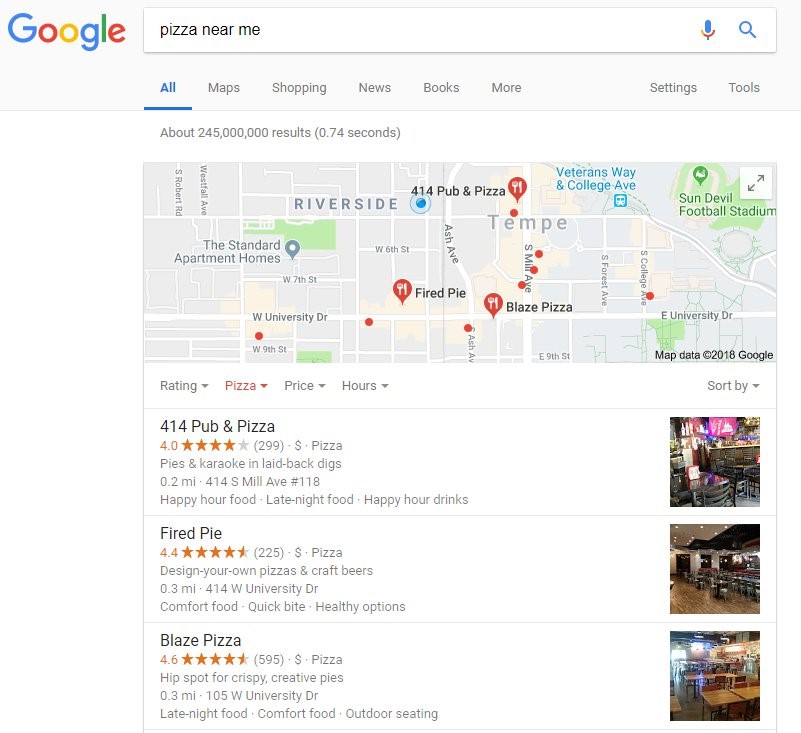
Google’s algorithm will continue to evolve and consider new factors when determining the value websites provide and how they should subsequently rank. This timeline can be especially useful for anyone interested in a more comprehensive look at how we got here.
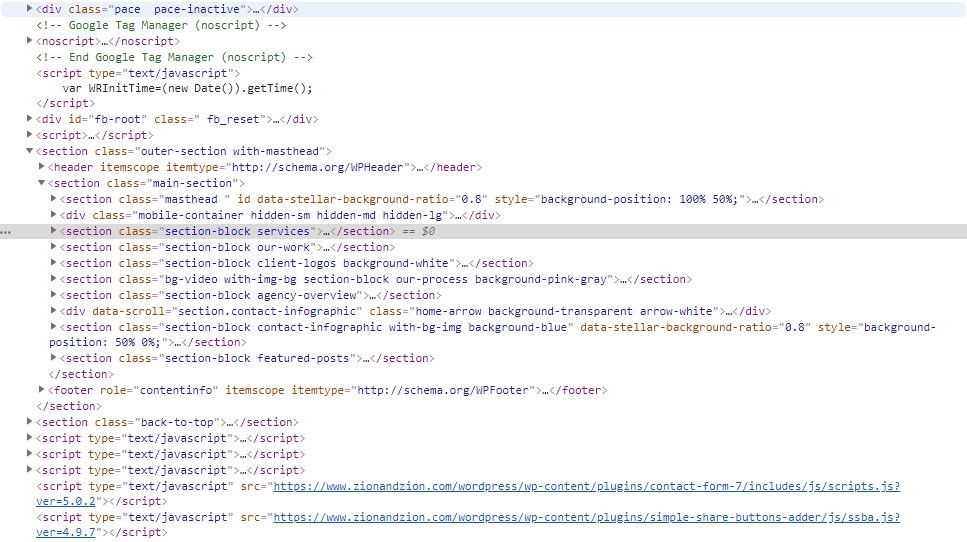
Search engines do not see a website like a person does, they see /code. Instead of seeing the color green, search engines see the /hex value of #008000. Instead of seeing an image, they see the file name and the alt attribute. /The source of a page can be viewed to see how a search engine sees the webpage. It is important to understand this when optimizing your site, even if something looks good visually, it may not have the proper optimized code.
These crawlers can be instructed where they can or cannot go with a robots.txt file and sitemaps which will be discussed later in this article.
On-Site SEO
Many factors can affect how a search engine ranks your site are within the code. Optimizing a website’s code is called on-site SEO. Think of a website as a car. Each of these factors are a part of the car, some more important than others, but all are needed to correctly run the car. Some of these techniques are a simple fix while others require access to the /ftp server.
URL
The URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is the address of your site. It’s what people will type in to get to the page and what the search engine displays as the destination. The URL should relate to the page’s contents. Some important factors in optimizing your URL include the following.
Shorter Is Better Than Longer
A short URL can be displayed completely on the search engine and social media networks. Avoid having many /levels of subdirectories, in many cases the best optimized URL has one subdirectory. Create short concise URLs for each page. When using the title of the post, remove unneeded filler words to keep the URL concise.
Use Keywords
When creating the file name (specific URL) for each page, be sure to use the focus keyword. Avoid oversaturating your URL with keywords. Instead, insert keywords where it reads naturally without forcing or overdoing it.
Use Hyphens, Not Underscores
It is a best practice to use hyphens (-) not underscores (_) to separate words in the URL.
Remove The Date
Some /Content Management Systems add the date to the final URL or place it in sub directories. This adds unneeded length to your URL. If displaying the date is important, implement it in the page itself instead of the URL.
Title Tag

The title tag is located in the /<head> of the webpage. It is used by the browser, search engine, and any bookmarking or sharing platform. It shows up as the name of your page. It is important to create titles that are unique, something made for users that entices them to click. It should also summarize the content of the page in a concise manner.
How Title Tags Show Up In The SERP
The title is the first impression your website makes on a person when doing a search. Perhaps the most important thing about the title of a page is that it is displayed prominently in the SERP. Different search engines will display different amounts of characters in their results. Title tags allow up to 70 characters on desktop and 78 characters on mobile. There’s two different philosophies when it comes to crafting title tags: keep it short and sweet, and shoot for ~50 characters—OR use up all the space you can as it’s essentially added real estate in SERPs. You may want to experiment and see what works best for your site.
Title Displayed In Browser
The title is also what is displayed in the title bar or tab of a browser and bookmarks. These often cut the title short. Knowing this, attempt to put most descriptive terms first and the brand terms (optional) last.
Meta Description

The description is a short paragraph that describes the content of a page. It is located in the /<head> of the webpage. Descriptions should be unique to the page it is on, written in a way to compel a user to visit the page and created for the user, not the search engine. The meta description is used by the search engine in the results page, appearing underneath the title and URL. If you do not create a description, the search engine may take a piece of content from the page and use it as the description. It is a best practice to keep the character count of the description under 156 or it will get cut off. Descriptions on mobile results are generally limited to 110 to 120 characters, so you may want to run shorter on specific pages.
Header Tags
UPDATE THIS IMAGE
Header or H tags are a way of structuring the content on your page both through code and /styles. They are used to create a hierarchy in the content within the page and help the piece flow. The content within these tags are more visible and are used by search engines when interpreting the purpose of the page. Search engines look at headers to take quick inventory and determine how much it relates to a search query. Due to spammy techniques, H tags have less value but are still considered essential with on-site SEO. H tags should be unique from page to page. Usually there should be a single H1 tag on a page with multiple H2, H3 or H4s—a natural hierarchy. Be sure that all H3s appear below a H2 and H4s appear below a H3 that is below a H2, all of which are below a H1 tag.
Linking
UPDATE THIS IMAGE
Linking is how users and search engines navigate through the internet. There are two types of links: follow and nofollow links. In the context of SEO, it helps to think about links as endorsements or professional recommendations. A follow (also known as dofollow) link is essentially a positive endorsement—the linking source is telling search engines I know and trust this site. A nofollow link is essentially a non-endorsement—here, the linking source is telling search engines I don’t know this site so please don’t associate me with it and potentially tarnish my good name! While most links (backlinks) provide value in SEO, the general consensus has been and remains: followed links are the gold standard.
Internal Linking
/Internal linking is a very important part of SEO. It benefits users by making your website easier to navigate, like aisles in a grocery store. It benefits search engines by helping them crawl your website and more readily interpret the content. Internal links should ideally be used to point toward pages that expand on or support the topic you are discussing—relevance to the linking keyword/overall subject is key. Don’t disorient your users.
Some key factors in optimizing internal linking is to use descriptive anchor text that gives the user an idea of where they will go if clicked. Anchor text like “click here” or the exact URL can be improved by using descriptive text instead. Be sure to include a /title attribute that describes the link.
External Linking
/External linking is very similar to internal linking, except it sends the user to another site. The same principles for internal linking apply here; link to a site that expands on a topic, use descriptive anchor text and title attributes. At Zion & Zion, we generally recommend external links open in a new tab or window so users can easily come back to your article.
Media Types
Implementing different forms of media on a page helps users digest your message in different manners. They also help break up the page from a mass of text. There are ways to optimize each type of media by using more than just text.
Images
Images are a great way to break up the text on a page. Give an example of a subject and optimize the page. Be sure to use images wherever you can to enhance your content. It is best to use images created or shot by the site’s owner. Search engines will rank your image higher in /image search if your images are unique to the site. Images allow for four separate ways to optimize; /alt attribute, /title attribute, file name, and an image caption. Optimizing the image for web use and saving as /progressive will ensure that the images do not increase page speed.
Videos
Videos are a great way to serve content in a manner other than text. They can be used almost anywhere you would place an image. Host a video on a third party hosting platform like YouTube, Vimeo, or /Wistia to increase video load speed and decrease the bandwidth on the site’s server. Utilizing schema.org micro data helps search engines know the content of your video. Unfortunately, search engines cannot listen to a video, so transcribing the video and placing this text on the page allows search engines to crawl the video content. Video transcriptions also help your website remain ADA compliant.
Canonicalization
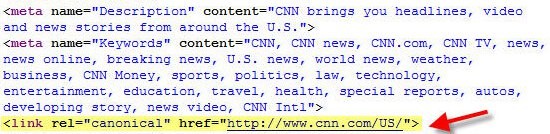
Canonicalization is creating a single page for a particular term or set of terms. Each page on a site should be focused to a particular set of terms so no other pages compete for that term. If there are pages competing, one should be set as the canonical page using the rel=canonical tag in the /<head> of the document. This allows search engines to serve the page you have designated to rank for a targeted set of terms.
Without canonicalization, multiple pages can compete for the same set of keywords. This can confuse the search engine and have a negative impact on both pages. Duplicate content can also be an issue if canonicalization is not implemented. This can lead to lower rankings due to the Google Panda update.
Crawl Issues

Ensuring that a site has no /400 status errors is important so pages that do not exist are not indexed. 302 temporary redirects should be reviewed to evaluate if the page will return. If not, change the code to a 301 permanent redirect.
Schema Microdata

/Schema is a micro format that Google and Microsoft created so search engines could easily digest a site and understand the different parts. It can and should be implemented through the entire page. It’s especially important to apply schema to your physical address if you operate a local business to improve your performance in local search results.
Sitemap
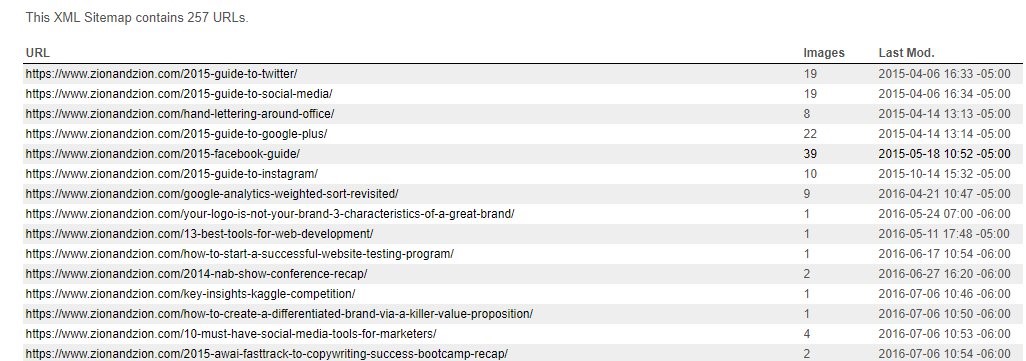
There are two types of /sitemaps and both are beneficial, one for users and one for search engines. A HTML sitemap is a sitemap created for users so they can easily find any page on the site. The XML sitemap is created for search engines and tells them what pages to crawl and index. The location of the XML sitemap should be placed in the robots.txt file on the website.
Robots.txt

You may not want every page of your website visible to the public. A robots file on the /root of the sites server tells search /bots where to go, restricting access to key areas. These are great for /CMS websites like WordPress because it can block the files used by the CMS from showing up in search. A link to the location of the XLM sitemap should be included in this file so the robots know where to find a list of pages to crawl.
.htaccess File
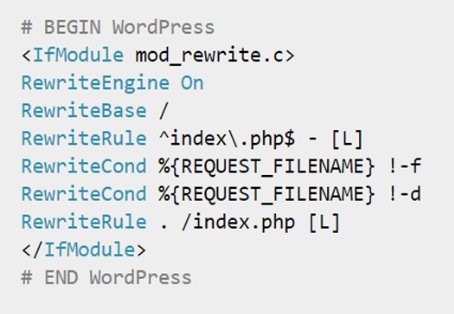
The htaccess file is a very powerful file that, when used correctly, can help optimize a page. Because this file is used prior to displaying the website’s content, if it is used incorrectly the website can act incorrectly or not at all. Not all servers support htaccess. Other tools like /Plesk or CPanel can be used to complete the same tasks. Some benefits of the htaccess file include:
- Created redirects
- Specifying /http or https for a page
- Forcing or omitting www.
- Removing trailing index files in the URL
- Pointing to a /404 page
Page Speed
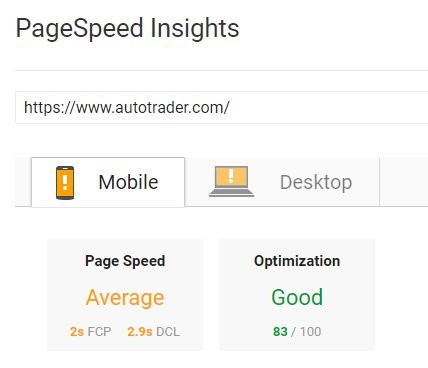
Page speed is now considered a critical aspect of SEO and essential to delivering a quality user experience. Users expect your page to load within three seconds—if it doesn’t, they’re more likely to abandon your site altogether. To optimize a page’s speed, follow these best practices:
- Enable compression on files
- Leverage Browser Caching
- Optimize images
- Minify JavaScript, CSS & HTML
- Use a /content delivery network
It’s important to test your pages for speed. Google’s PageSpeed Insights is a free tool you can use for a quick snapshot of your performance and get suggestions on areas to fix.
Off-Site SEO
Off-site SEO are the external factors that impact your rankings — things like backlinks, social media and local listings. Here’s a brief overview of the major off-site factors that influence SEO:
Backlinks
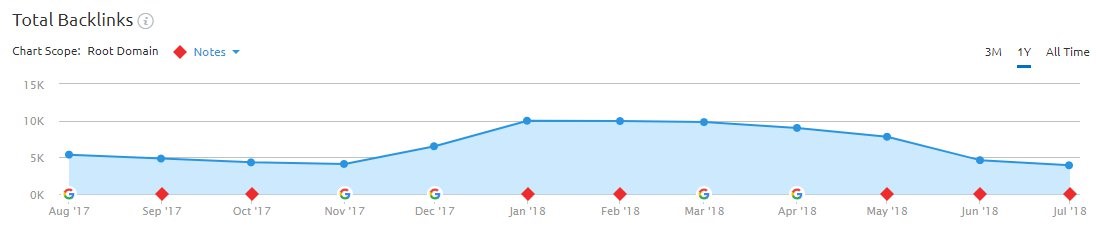
When a website links to a website it is called a backlink. These links can be looked at like a vote from one site for another site. The more authoritative the site linking to the other, the more valuable the link. Not all backlinks are created equal—there’s a big difference between receiving a link from Adweek and receiving a link from your cousin’s blog. The more familiar Google is with a website, the more trusted backlinks the linking source they themselves have—generally means the more powerful the link becomes.
Links should come naturally. As a site produces quality content, other sites will link to it. Some factors to links that are important are the anchor text, the page the link is pointing to, the authority of the domain linking, and the ratio of links per domain.
Social Media

Social media is a great way to increase awareness of your site and brand. It can be used to spread content, so it is more likely to earn links. While search engines have stated that social signals are not in the algorithm, some searches do use feedback from social media to order and personalize rankings.
Social media accounts and posts can rank highly, allowing a site to take up more of the SERP with more than their domain. For best rankings, be sure to post regularly on social and create a large network that shares your content.
Local Listings
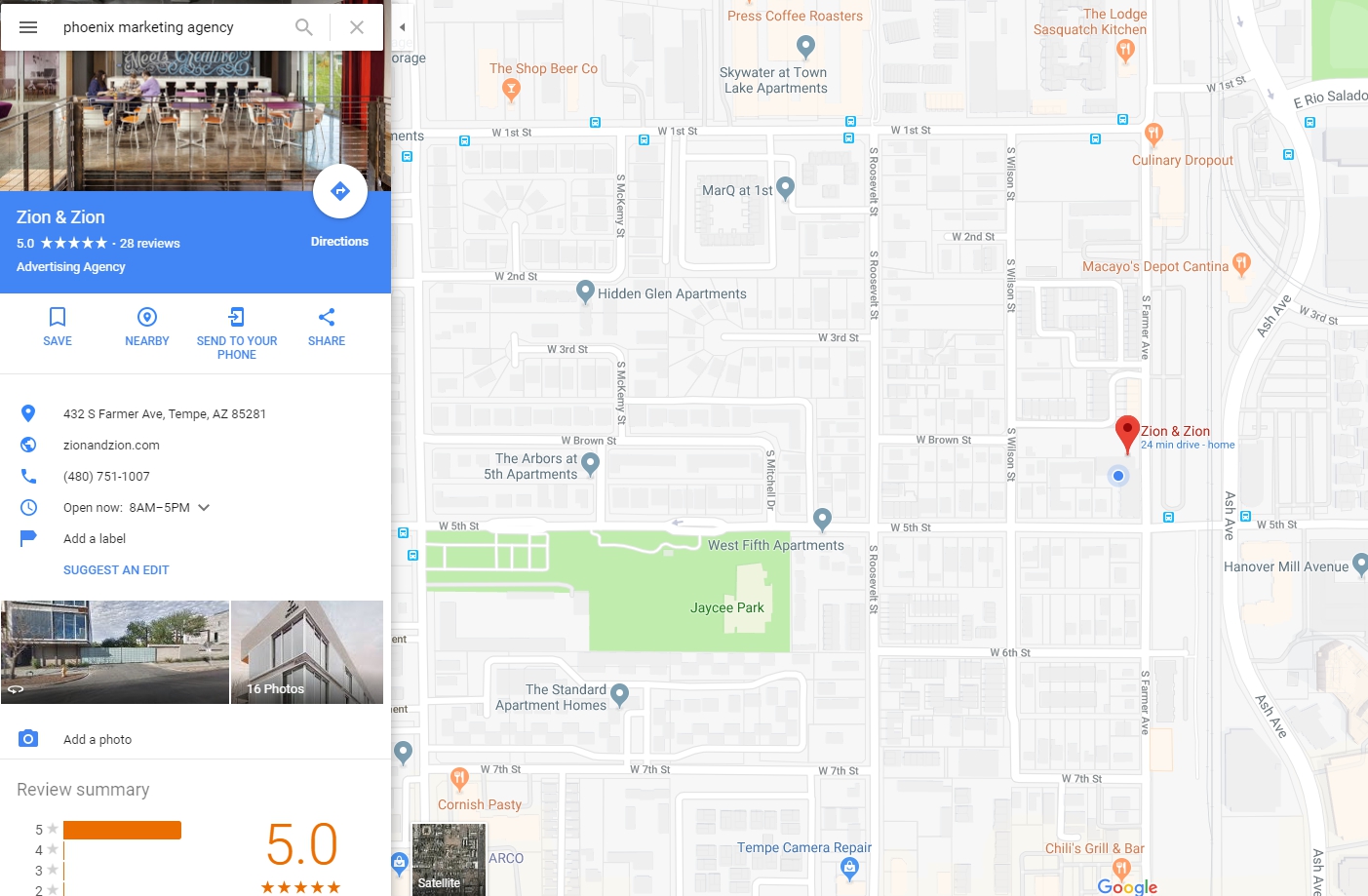
Local listings can also rank highly in the SERP. There are a variety of listing sites throughout the web. It is important that all of these listing sites have the accurate NAP information for your business and website. These sites can drive traffic to your site and provide reviews.
White Hat vs Black Hat SEO
The main difference between white hat and black hat SEO is that black hat is used to manipulate search engines to garner better results, while white hat SEO stays within search engine guidelines. Ranking highly is difficult and takes time, be wary of someone who promises to gain top rankings in search quickly.
White Hat SEO
White hat SEO are techniques of optimization that follow search engines’ guidelines. All of the topics that are discussed in this article can be considered white hat. The key is to follow best practices, so your site is finely tuned for search engine use and earns quality social shares and links to the site.
White hat SEO takes a lot of work and time. Doing a single thing like optimizing title tags will not get a site to the top spot in search. White hat SEO requires a holistic approach to improve a site user’s experience, crawlablity and footprint on the web through social media and backlinks. When starting a new campaign, expect 6-9 months for results to truly show.
The best advice for anyone who is trying to improve rankings is to create content that people will read and enjoy. Turn the site into a resource for the world and establish the brand as an expert in the field so people will trust and utilize the information and services provided. Then, tell everyone about it through all available channels.
Black Hat SEO
Black hat techniques may work quickly but can result in the site being de-indexed in the most extreme cases, essentially removing the site from search results altogether. By manipulating rankings through unethical means, rankings can soar but can also hinder a domain forever.
Some black hat techniques to avoid include the following.
Bad Link Building
- Link farms
- Directories
- Guest blogging
- Comment spam
- Trackbacks
- Forums
- Sitewide Links
Website Scraping / Mirroring
Taking something from one site and putting it on yours as if it was your own.
Cloaking / Doorway Pages
Making the page appear one way to a search engine but a different way to a user.
Hidden Text
Placing text off the page or having it be the same color as the background.
Hijacked Site
Taking over someone’s site and placing links on it.
Negative SEO
Doing black hat techniques to someone else’s site so they get penalized.
Conclusion
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is a complex science that has an end goal of improving a website’s ranking in search engines. There are many aspects to optimization, both on-site and off-site. Success can be had by creating a strategy that improves the site for search engines, creating unique and quality content and earning shares and links throughout the web.
SEO Resources
For anyone new to SEO, this is a must read.
/Google Webmaster Central Blog
Information straight from the horse’s mouth. A great place to find out what is new with search.
Google Webmaster Central YouTube Channel
Videos from the Google team that help webmasters understand how Google works.
The head of Google’s Search Spam fighting division’s personal blog.
A fantastic resource for SEO. The Moz team regularly pushes out great content to their blogs.
A site with the latest updates in search.
List of Search Engines
SEO Resources On Google Plus
- Google Webmasters
- Google Analytics
- Rand Fishkin
- Danny Sullivan
- Search Engine Watch
- Moz
- Search Engine Round Table
- Search Engine Journal
- Cyrus Shepard
- Neil Patel
- Will Reynolds
- Arnie Kuenn
- Gianluca Fiorelli
- Bill Slawski
- Aaron Bradley
- Jenny Halasz
- Mark Thaphagen
- Dana Lookadoo
- SEO
- Dejan SEO
- Internet Marketing Ninjas
- SEO By The Sea
- SEO Theory
- Traffic Generation Cafe
- SEO Takeaways
- Majestic SEO
- SEER Interactive
WordPress SEO Plugins
The best plugin for optimizing titles, descriptions, canonical pages and setting social media meta data.
Does the same things as Yoast, but not as well.
This plugin will improve your page speed by minifying code and connecting the site to a /Content Delivery Network.
Easy redirection of pages on the site. Allows tracking or redirects to see what pages are visited the most.
Easily create sitemaps for the website.
OLD POST
Search Engine Optimization Overview
Search Engine Optimization, also known as SEO, is how a website can be improved or optimized so it ranks higher by search engines. By improving a site’s visibility to search engines and focusing on how the search engine algorithm measures a website, a site can have better results in the /Search Engine Results Page (SERP). The forever changing landscape of Google Updates that improve search results has created a shift in strategy. Cheating the system by using /black hat techniques is getting sites penalized and de-indexed. Now one must create content that is searchable, shareable and linkable that is not only unique to the site but also a unique and expert opinion on the topic. It is vital to put a focus on creating websites and pages for Should say “users, not websites for search that try to “trick” the search engines.
[quicknav type=list]
How Search Engines Work
Search engines use robots/spiders/crawlers to scan the internet, indexing the pages in a large database usually /relational or /BigTabe. These crawlers go from site to site following the links on each site, both internal and external. These sites are then sorted by their content, usability and other factors.
Search Engine Algorithm
When a keyword is searched for on a search engine, an algorithm that takes /over 200 factors into consideration is used to query the database to find the best results. These algorithms are constantly being tested and improved so that the best results can appear in the search engine results page. In recent years, /Google has created updates to fight spam and serve the best webpages possible. Some things that these updates focus on are duplicate content, paid links and using black hat techniques.
How Search Engines See Your Site

Search engines do not see a website like a person does, they read the /code. Instead of seeing the color green they see the /hex value of #008000. Instead of seeing an image they see the file name and the alt attribute. /The source of a page can be viewed to see how a search engine sees the webpage. It is important to understand this when optimizing your site, even if something looks good visually, it may not have the proper optimized code.
These crawlers can be instructed where they can or cannot go with a robots.txt file and sitemaps which will be discussed later in this article.
On-site Optimization
Many factors that can affect how a search engine ranks your site are within the code. Optimizing a website’s code is called On-Site Optimization. Think of a website as a car, each of these factors are a part of the car, some more important than others but all are needed for the car to run correctly. Some of these techniques are a simple fix while others require access to the /ftp server.
URL
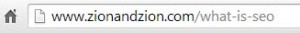
The /URL or URI is the address of your site. It is what people will type in to get to the page and what the search engine displays as the destination. The URI should relate greatly to the page’s contents. Some important factors in optimizing the URL are:
Shorter is better than longer
A short URL can be displayed completely on the search engine and social media networks. Avoid having many /levels of subdirectories, in many cases the best optimized URL has one subdirectory. Create short concise URLs for each page. When using the title of the post, remove unneeded filler words to keep the URL concise.
Use keywords
When creating the file name (specific URL) for each page, be sure to use the focus keyword. Avoid over saturating your URL with keywords. Instead, insert keywords where it reads naturally without forcing or overdoing it.
Use – not _ to separate words
It is a best practice to use hyphens (-) not underscores (_) to separate words in the URL.
Keep the date out
Some /Content Management Systems will add the date to the final URL or place it in sub directories. This adds unneeded length to your URL. If displaying the date is important, implement it in the page itself instead of the URL.
Title Tag
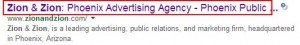
The title tag is located in the /<head> of the webpage. It is used by the browser, search engine and any bookmarking or sharing platform. It shows up as the name of your page. It is important to create titles that are unique, will compel someone to click and are written for users, not search engines. It should also summarize the content of the page in a concise manner.
How Title Tags Show Up in the SERP
The title is the first impression your website makes on a person when doing a search. Perhaps the most important thing about the title of a page is that it is displayed prominently in the SERP. Different search engines will display different amounts of characters in their results. It is a best practice to have your titles under 70 characters. I like to keep them /around 52 characters, this way the title is long enough to explain the page’s content but is short enough not to get cut off.
Title Displayed in Browser
The title is also what is displayed in the title bar or tab of a browser and bookmarks. These often cut the title short. Knowing this, attempt to put most descriptive terms first and the brand terms (optional) last.
Meta Description

The description is a short paragraph that describes the content of a page. It is located in the /<head> of the webpage. Descriptions should be unique to the page it is on, written in a way to compel a user to visit the page and created for the user, not the search engine. The meta description is used by the search engine in the results page appearing underneath the title and URL. If you do not create a description, the search engine may take a piece of content from the page and use it as the description. It is a best practice to keep the character count of the description under 156 or it will get cut off.
Header Tags
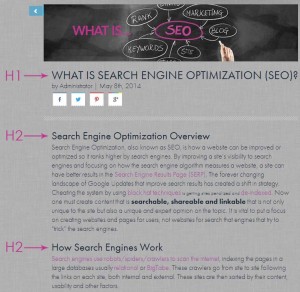
Header or H tags are a way of structuring the content on your page both through code and /styles. They are used to create a hierarchy in the content within the page to help the piece flow and be broken up into segments. The content in these tags are more visible on the page and are more important than other text. Search engines will take the headers and use them in the algorithm. Due to spammy techniques, H tags are less important to SEO than before. H tags should be unique from page to page. Usually there should be a single H1 tag on a page with multiple H2, H3 or H4s. Use these in a hierarchy. Be sure that all H3s appear below a H2 and H4s appear below a H3 that is below a H2, all of which are below a H1 tag.
Linking

Linking is how users and search engines navigate through the internet. There are two types of links: follow and nofollow. The difference being that an attribute of nofollow is added to the link, letting search engines know that this link should not pass /page rank. A follow link sometimes called dofollow, is a link that is placed on a site consciously as an editorial decision. They are meant to improve the user’s experience and should not be paid for or used for advertisements.
Internal linking
/Internal linking is a very important part of SEO. It is beneficial to the user allowing them to stay on your website to find out more information. It is beneficial to search engines by helping pass page rank throughout the site and assisting them in crawling the website. Ideally links would point to pages that expand upon the topic you are discussing. This allows the page to cover a topic without diving deep or going off on a tangent.
Some key factors in optimizing internal linking is to use descriptive /anchor text that gives the user an idea of where they will go if clicked. Anchor text like “click here” or the exact URL can be improved by using descriptive text instead. Be sure to include a /title attribute that describes the link. The link should open in a new window or tab, this way users can keep reading your article or come back to it easily.
External Linking
/External linking is very similar to internal linking except it takes a user off of the site and sends them to another site. These sites should be authoritative and a primary source of information. The same principles for internal linking apply here; link to a site that expands on a topic, use descriptive anchor text and title attributes and have the link open in another window.
Media Types
Implementing different forms of media on a page helps users digest your message in different manners. They also help break up the page from a mass of text. There are ways to optimize each type of media by using more than just text.
Images
Images are a great way to break up the text on a page. Give an example of a subject and optimize the page. Be sure to use images wherever you can to enhance your content. It is best to use images created or shot by the site owner. Search engines will rank your image higher in /image search if your images are unique to the site. Images allow for four separate ways to optimize; /alt attribute, /title attribute, file name and an image caption. Optimizing the image for web use and saving as /progressive will ensure that the images do not increase page speed.
Videos

Videos are a great way to serve content in a manner other than text. They can be used almost anywhere you would place an image. Host a video on a third party hosting platform like YouTube, Vimeo or /Wistia to increase video load speed and decrease the bandwidth on the site’s server. Utilizing schema.org micro data helps search engines know the contents of your video. Unfortunately search engines cannot listen to a video so transcribing the video and placing this text on the page allows search engines to crawl the video content.
Canonicalization

Canonicalization is creating a single page for a particular term or set of terms. Each page on a site should be focused to a particular set of terms so that no other pages compete for that term. If there are pages competing, one should be set as the canonical page using the rel=canonical tag in the /<head> of the document. This allows search engines to serve the page you have designated to rank for a targeted set of terms.
Without canonicalization, multiple pages can compete for the same set of keywords. This can confuse the search engine and cause them to rank both pages poorly instead one well. Duplicate content can also be an issue if canonicalization is not implemented. This can lead to lower rankings due to the Google Panda Update.
Crawl Issues
Ensuring that a site has no /400 status errors is important so pages that do not exist are not indexed. 302 temporary redirects should be reviewed to evaluate if the page will return, if not change the code to a 301 permanent redirect.
Schema Microdata
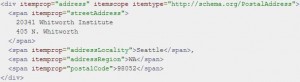
/Schema is a micro format that Google and Microsoft created so search engines could easily digest a site and understand the different parts. It can and should be implemented through the entire page. It is especially important to schema your address to help with local search.
Sitemap
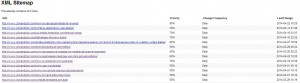
There are two types of /sitemaps, both are beneficial, one for users and one for search engines. A HTML sitemap is a sitemap created for users so they can easily find any page on the site. A XML sitemap is created for search engines telling them what pages to crawl and index. XML sitemaps can be created for specific content like blog posts, images and videos. The location of the XML sitemap should be placed in the robots.txt file on the website.
Robots.txt
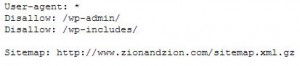
A robots file on the /root of the sites server that tells /robots (the scripts that search engines use to crawl a site) where not to go. It is used to prevent undesired pages to appear in search. These are great for /CMS websites like WordPress because it can block the files used by the CMS from showing up in search. A link to the location of the XLM sitemap should be included in this file so the robots know where to find a list of pages to crawl.
.htaccess file
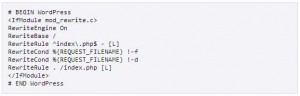
The htaccess file is a very powerful file that when used correctly can help optimize a page. Because this file is used prior to displaying the website’s content, if it is used incorrectly the website can act incorrectly or not at all. Not all servers support htaccess. Other tools like /Plesk or CPanel can be used to complete the same tasks. Some benefits of the htaccess file include:
- Created redirects
- Specifying /http or https for a page
- Forcing or omitting www.
- Removing trailing index files in the URL
- Pointing to a /404 page
Page Speed
Load speed of a webpage is and will continue to be a growing part of the search algorithm. Slow pages frustrate users causing them to bounce and return to search results. To optimize a page’s speed, follow these best practices:
- Enable compression on files
- Leverage Browser Caching
- Optimize images
- Minify JavaScript, CSS & HTML
- Use a /content delivery network
Off-site Optimization
There are factors that can impact the rankings of a website that are not actually on the website. External factors like links, social media and local listings can boost the rankings for a specific location or term.
Backlinks
When a website links to a website it is called a backlink. These links can be looked at like a vote from one site for another site. The more authoritative the site linking to the other, the more valuable the link. Links pass /Page Rank from one page to another; this Page Rank pass is what helps websites rank higher. Backlinks have a large impact on the search engine algorithm and have been utilized in black hat techniques so much that /Google has updated their algorithm to lower the ranking of sites that have participated in link placement.
Links should come naturally. As a site produces quality content, other sites will link to it. Some factors to links that are important are the anchor text, the page the link is pointing to, the authority of the domain linking and the ratio of links per domain.
Social Media
Social media is a great way to increase awareness of your site and brand. It can be used to spread content so it is more likely to earn links. While search engines have stated that social signals are not in the algorithm, some searches do use feedback from social media to order and personalize rankings.
Social media accounts and posts can rank highly, allowing a site to take up more of the SERP with more than their domain. For best rankings, be sure to post regularly on social and create a large network that shares your content.
Local Listings
Local listings can also rank highly in the SERP. There are a variety of listing sites throughout the web. It is important that all of these listing sites have the accurate information for your business and website. These sites can drive traffic to your site and provide reviews.
Google Authorship
/Google is now providing a service that tracks all the content created by a specific person to a Google+ account. This will allow posts to have an established author created to rank higher and more quickly than if authorship was not implemented. It also can display an image next to the search results which may lead to higher click through rates.
Update
Google Authorship is now deprecated and no longer active.
White Hat vs Black Hat SEO
The main difference between white hat and black hat SEO is that black hat is used to manipulate search engines to garner better results, while white hat SEO stays within search engine guidelines. Ranking highly is difficult and takes time, be wary of someone who promises to gain top rankings in search quickly.
White Hat SEO
White hat SEO are techniques of optimization that follow search engines’ guidelines. All of the topics that are discussed in this article can be considered white hat. The key is to follow best practices so your site is finely tuned for search engine use and earns quality social shares and links to the site.
White hat SEO takes a lot of work and time. Doing a single thing like optimizing title tags will not get a site to the top spot in search. White hat SEO requires a holistic approach to improve a site user’s experience, crawlablity and footprint on the web through social media and backlinks. When starting a new campaign, expect 6-9 months for results to truly show.
The best advice for anyone who is trying to improve rankings is to create amazing content that people will read and enjoy. Turn the site into a resource for the world and establish the brand as an expert in the field so people will trust and utilize the information and services provided. Then tell everyone about it through all available channels.
Black Hat SEO
Black hat techniques may work quickly but can result in the site being de-indexed forever, never ranking on a search engine again. By manipulating rankings through unethical means, rankings can soar but can also hinder a domain forever.
Black hat SEO has given Search Engine Optimizers like myself a bad name. These companies or professionals that promise the world quickly, then leave a site owner worse off than before they started, have given our industry a black eye. Some black hat techniques to avoid are:
Bad link building
- Link farms
- Mommy bloggers
- Directories
- Guest blogging
- Comment spam
- Trackbacks
- Forums
- Sitewide Links
Website Scraping / mirroring
Taking something from one site and putting it on yours as if it was your own.
Cloaking / doorway pages
Making the page appear one way to a search engine but a different way to a user.
Hidden text
Placing text off the page or having it be the same color as the background.
Hijacked site
Taking over someone’s site and placing links on it.
Negative SEO
Doing black hat techniques to someone else’s site so they get penalized.
Conclusion
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is a complex science that has an end goal of improving a website’s ranking in search engines. There are many aspects to optimization, both on-site and off-site. Success can be had by creating a strategy that improves the site for search engines, creating unique and quality content and earning shares and links throughout the web.
SEO Resources
- /Google’s SEO Starter’s Guide
- For anyone new to SEO, this is a must read.
- /Google Webmaster Central Blog
- Information straight from the horse’s mouth. A great place to find out what is new with search.
- Google Webmaster Central YouTube Channel
- Videos from the Google team that help webmasters understand how Google works.
- /Matt Cutts Website
- The head of Google’s Search Spam fighting division’s personal blog.
- /Moz Blog
- A fantastic resource for SEO. The Moz team regularly pushes out great content to their blogs.
- /Search Engine Land
- A site with the latest updates in search.
List of Search Engines
[one_fourth]
[/one_fourth][one_fourth]
[/one_fourth][one_fourth]
[/one_fourth][one_fourth_last]
SEO Resources on Google Plus
[one_third]
- Google Webmasters
- Google Analytics
- Matt Cutts
- Rand Fishkin
- Danny Sullivan
- Search Engine Watch
- Moz
- Search Engine Round Table
- Search Engine Journal
- Ben Holland
[/one_third][one_third]
- Cyrus Shepard
- Neil Patel
- Will Reynolds
- Arnie Kuenn
- Gianluca Fiorelli
- Bill Slawski
- Aaron Bradley
- Jenny Halasz
- Mark Thaphagen
- Dana Lookadoo
[/one_third][one_third_last]
- SEO
- Dejan SEO
- Internet Marketing Ninjas
- SEO By The Sea
- SEO Theory
- Traffic Generation Cafe
- SEO Takeaways
- Majestic SEO
- SEER Interactive
WordPress SEO Plugins
- Yoast SEO Plugin
- The best plugin for optimizing titles, descriptions, canonical pages and setting social media meta data.
- All in one SEO Pack
- Does the same things as Yoast, but not as well.
- W3 Total Cache
- This plugin will improve your page speed by minifying code and connecting the site to a /Content Delivery Network.
- /Redirection
- Easy redirection of pages on the site. Allows tracking or redirects to see what pages are visited the most.
- /Google XML Sitemaps
- Easily create sitemaps for the website.
